Projectile mechanics are a set of rules which apply to some (or all) projectile weaponry in the Battlefield series. Most of them are artificial representations of real-life laws of physics. This page catalogs those mechanics and their effects on the game.
In the Battlefield series, bullets, shells, grenades, et cetera are represented as game items, rather than abstract concepts such as hitscans.
Velocity
Travel time, also known as velocity is a representation of how quickly a bullet or shell moves through the air. All of the main Battlefield games, from Battlefield 1942 onward, possess velocity for all weapons. It's typically defined on a per-weapon basis, and determines how quickly the bullet will reach its target.
As a result of velocity, in order to accommodate for a target's movements a player will typically have to lead their target -- that is, aim ahead of the target's direction -- in order to successfully make contact.
Projectile arc
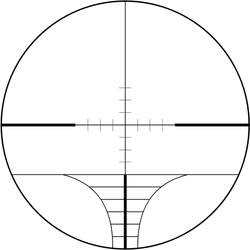
An modern rangefinder reticle for bullet drop
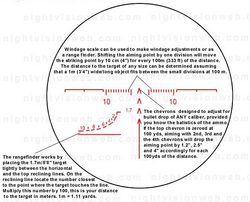
Common scope reticle attached on the SVD to adjust for bullet drop over range
When a projectile is set into motion, gravity pulls on the projectile at the same time as the momentum behind the projectile keeps it moving forward. The result is an arc-shaped trajectory.
The first Battlefield games lack bullet physics for all weapons but shells, rocket launchers, thrown weapons, and handguns. In the later games, standard projectiles as well as rockets and shells also suffer from projectile arc. In the games, the projectile physics concerned use the standard acceleration due to gravity, ~9.81ms−2, for the calculation of bullet drop.
Battlefield 1942
In Battlefield 1942, projectile physics are included only for shells, handguns, anti-tank rocket launchers, and thrown weapons. Although spread can give the sense of standard firearms having bullet physics, this is not an example of a projectile arc; tank shells and the Bazooka and Panzerschreck, however all have very noticeable arcs in their trajectory.
Battlefield Vietnam
Projectile arc in Battlefield Vietnam remains the same as its predecessor's counterpart. Only tank shells and rocket launchers are afflicted by projectile arc.
Battlefield 2
In Battlefield 2, projectile arc is added to the series for small-caliber weapons: there is a considerable amount of bullet drop over long distances. Combined with the fact that there is always a small amount of spread with the sniper rifles, it can make predicting a bullet's long-range trajectory near-impossible at distances beyond several hundred meters, as the potential area in which the bullet may land increases exponentially with distance.
Additionally, rockets that are no longer being guided, tank shells, and grenade launcher grenades suffer from considerable arc in their trajectory, although it is not as difficult to predict their trajectory compared to the conventional firearms due to their lack of spread.
Battlefield 2142
In Battlefield 2142, projectile arc mainly affects cannons (tank, Titan defense guns), mortars on the APCs, PK-74 AR-Rockets, and sniper rifle rounds. Even then, only snipers using the DysTek Hi-Scope x4 at maximum magnification will notice significant drop. The Engineer's basic main weapon (Mitchell AV-18 or Sudnik VP) and the SAAW 86 Anti-Air) experience drop when the rounds are not guided.
Rounds from the Rorsch Mk-S8 experience no noticeable drop, as they are fired at extremely high speed.
Anti-air rockets fired from the Rorsch Kz-27 or battlewalker anti-air turrets will actually arc slightly upward when dumb-fired.
Battlefield: Bad Company
In Battlefield Bad Company, projectile arc is present for both grenade launchers and tank shells (as well as the homing dart gun), though it is absent for conventional firearms.
Battlefield 1943
Like the first Bad Company game, projectile arc for small-caliber weapons is once again absent. However, for tank shells and the rocket launcher, there is a noticeable, if considerably flatter in trajectory compared to the older games in the series.
Battlefield: Bad Company 2

Bullet drop in Bad Company 2
In Battlefield: Bad Company 2, bullet drop is present for all weapons, including rocket launchers. While all weapons suffer from bullet drop, it is most prevalent with the Recon kit, due to the magnified scope magnifying the bullet drop when aiming.
Countering bullet drop is simple - players need only to guess the range of the target and then adjust the elevation of their shots carefully to negate the effect. Snipers are the easiest to do so with this, with weapons such as the M24 and the GOL having open sight reticles, making adjusting the shot easy, while the reticle for the SVU and the SV-98 are harder to use, but still potent.
On maps such as Laguna Alta and urban/woodland portions of most other maps, the typical ranges of combat make the benefits for adjusting for bullet drop negligible. If in doubt as to aiming a shot at medium ranges, players should usually avoid risk and aim directly for the head - doing so will usually result in a hit to the target's body, instead of the bullets sailing over the target's head if the range guess was wrong.
[[Video:M95 Sound and Bullet Drop in Del Toro (Campaign) in Bad Company 2|300px|thumb|left|The M95's bullet drop over long range]]
Battlefield 3
Bullet drop returns again in Battlefield 3. It is much more noticeable this time around due to the large maps like Operation Firestorm and Caspian Border, and the ability of the Frostbite 2 game engine to draw much further than the Refractor engine last used in Battlefield 2142. Players can also see their own bullet tracers.
In Campaign and Co-op, enemies are rarely encountered at ranges where bullet drop would affect small weapons. Tank shells notably ignore gravity in the single player, as can be seen in the mission Thunder Run.
Scopes used on in-game firearms may not reflect their real-world use. Actual weapon sights are "zeroed" on a point a set distance away (e.g. 300 meters) where projectiles from the weapon are expected to cross. The scope is thus pointing slightly downward from the axis of the gun barrel. Inside of the zeroed distance, the projectile is slightly higher than the scope's axis, a trivial matter given the size of the target.
In game, when aiming down sight or in a vehicle, the game engine actually emits the projectile from the scope, ensuring that the weapon will impact on target regardless of the position of the barrel (which may be clipping through an object). The projectile's initial motion is parallel to the scope's axis.
Battlefield 4
Bullet drop returns in Battlefield 4 and functions similarly to its predecessor Battlefield 3, but incorporates adjustable zeroing for Sniper Rifles and DMRs, as well as fixed zeroing on the SMAW and RPG-7V2.
Rangefinders are also introduced.
Spread
Spread is an abstraction of various real-life conditions which can cause a weapon's round to not go where the perceived aimpoint is. When a weapon is fired, there's essentially a random chance for it to go in any direction within a small area, called the cone of fire. When the weapon is fired, the engine chooses a direction and the round is then completely independent of the weapon's spread (although other mechanics may factor into precisely where the round goes, such as projectile arc). It is to standard small arms what sway is to sniper rifles, although sniper rifles may also be subject to spread.
Sway
Sway is a representation of the breathing and movement a shooter has on the exact aimpoint of his weapon. While in-game, the weapon might sway visually when at rest or zoomed, this typically has no effect on the aimpoint of the weapon. It is mainly with sniper rifles that sway comes into play -- the scope's reticule will move and shift on its own, changing where the precise aimpoint of the player's weapon is. While the user may also be subject to spread (and thence might be able to achieve a hit even when the reticule isn't actually on a given target), sway will usually be the larger factor.
| |||||||||||||||||


